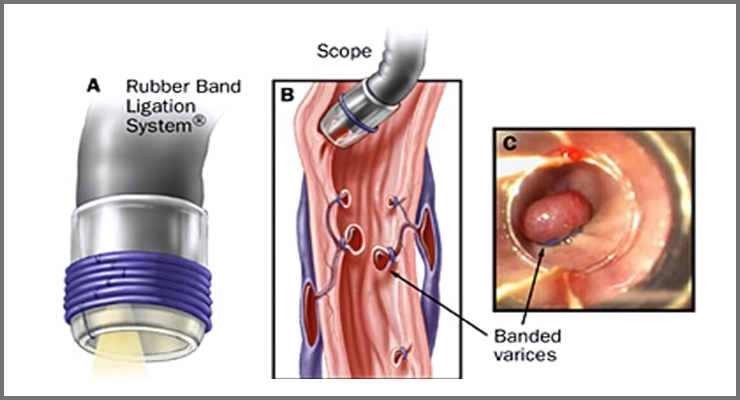
Variceal band ligation or banding
Variceal band ligation is a therapeutic procedure used to treat bleeding from varices, which are abnormally dilated veins typically found in the esophagus or stomach. Variceal bleeding is a serious complication of liver cirrhosis, portal hypertension, or other liver diseases. During the procedure, a special device attached to the endoscope is used to place small rubber bands around the varices, causing them to constrict and ultimately stop the bleeding.
Variceal band ligation is usually performed as an emergency procedure to control acute bleeding episodes or as a preventive measure to reduce the risk of future bleeding episodes. The procedure is generally safe and effective but may be associated with certain risks such as esophageal injury, bleeding, or perforation. Patients undergoing variceal band ligation may require ongoing monitoring and management of their liver disease to prevent recurrent bleeding.
Treatment involves:
- Placement of rubber bands around bleeding varices to constrict them and stop bleeding
- Prevention of recurrent bleeding by ligation of additional varices as needed
- Monitoring for complications such as esophageal injury, bleeding, or perforation
