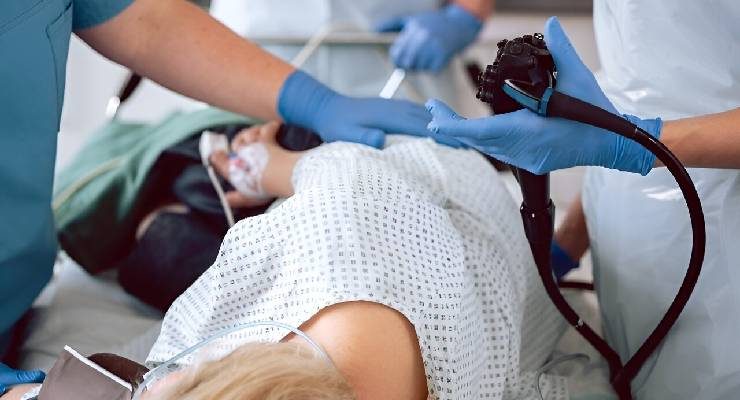
Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy is a procedure similar to colonoscopy but focuses on examining the lower portion of the colon, specifically the sigmoid colon and rectum. It is often used for screening purposes or to investigate symptoms such as rectal bleeding, changes in bowel habits, or abdominal pain. Sigmoidoscopy can help detect conditions such as colorectal cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, hemorrhoids, or diverticulosis.
Unlike colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy does not require sedation in most cases. The procedure is performed using a flexible sigmoidoscope, which is inserted through the anus and advanced into the sigmoid colon. The sigmoidoscope is equipped with a camera and light source, allowing the doctor to visualize the lining of the colon and rectum. If abnormalities are detected, further evaluation or treatment may be necessary.
Treatment during sigmoidoscopy may involve:
- Removal of polyps in the sigmoid colon or rectum
- Biopsy to evaluate inflammation, infection, or other abnormalities
- Hemostasis (control of bleeding) for rectal bleeding or vascular abnormalities
- Treatment of conditions such as hemorrhoids or anal fissures
