Endoscopy Ultrasound (EUS) Treatment In Pune
Endoscopy Ultrasound (EUS)
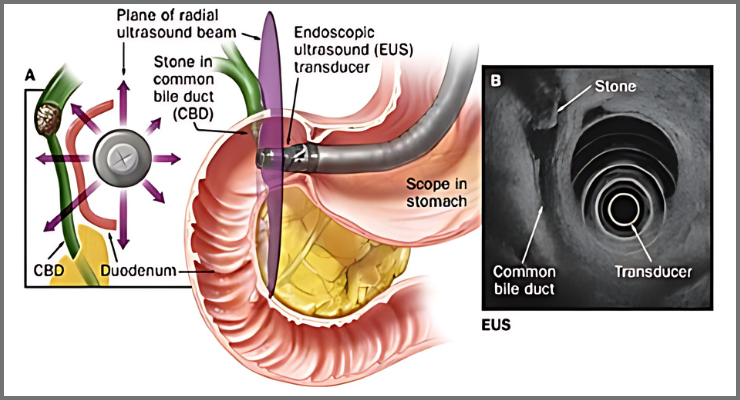
Definition: Endoscopy Ultrasound (EUS) combines endoscopy and ultrasound to obtain detailed images and information about the digestive tract and surrounding tissues and organs. The endoscope used in EUS has an ultrasound probe at its tip, which allows for high-resolution imaging.
Indications:Staging of cancers (esophageal, gastric, pancreatic, rectal)Evaluating the pancreas for cysts, tumors, or chronic pancreatitisAssessing bile duct and gallbladder diseasesInvestigating submucosal lesions in the GI tractGuiding fine-needle aspiration (FNA) for biopsy
Procedure:
Preparation: Patients are sedated or given anesthesia.
Insertion: The endoscope is inserted through the mouth (or rectum for lower GI tract evaluation).
Imaging: Ultrasound waves are emitted from the probe, creating detailed images of the digestive tract and nearby structures.
Biopsy: If needed, a fine needle can be passed through the endoscope to take tissue samples from abnormal areas.
Benefits:Provides detailed images of the digestive tract and surrounding structures Minimally invasive compared to surgical options Allows for precise biopsy and staging of tumors Useful in evaluating the pancreas and biliary system, which are difficult to assess with other imaging techniques
Risks:Discomfort or sore throat Bleeding, especially if a biopsy is taken Infection Perforation of the GI tract Pancreatitis (particularly with pancreatic EUS)
Recovery:Patients usually recover quickly from EUS with mild sedation. They can often go home the same day, but should not drive or operate machinery until the sedative effects have fully worn off. Mild sore throat or bloating can occur but typically resolves within a day.
